Notebooks
Premium
Trends
BioTuring
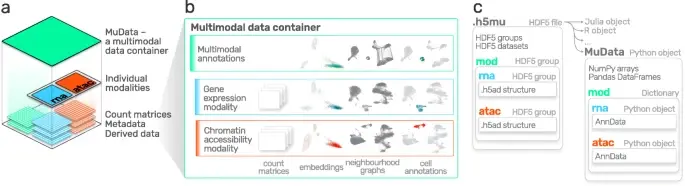
Advances in multi-omics have led to an explosion of multimodal datasets to address questions from basic biology to translation. While these data provide novel opportunities for discovery, they also pose management and analysis challenges, thus motiva(More)