Notebooks
Premium
Trends
BioTuring
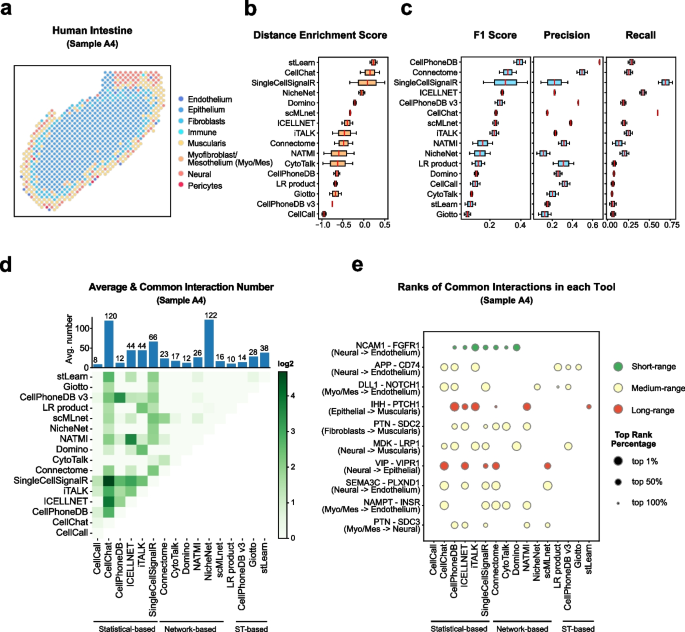
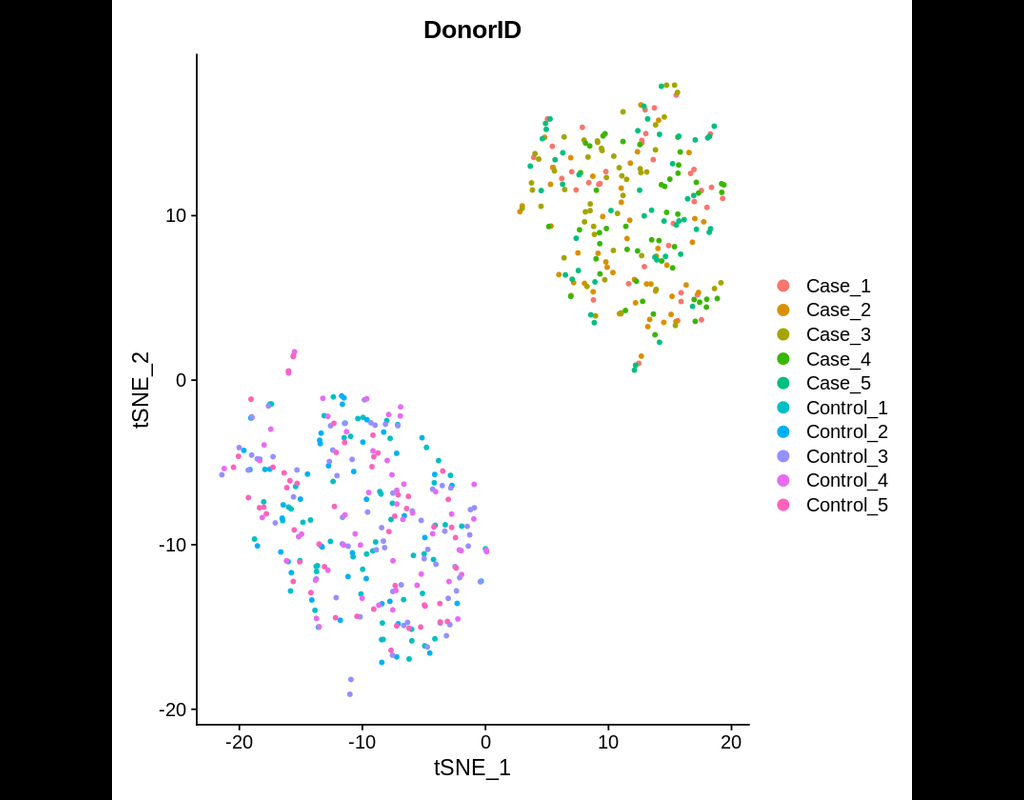
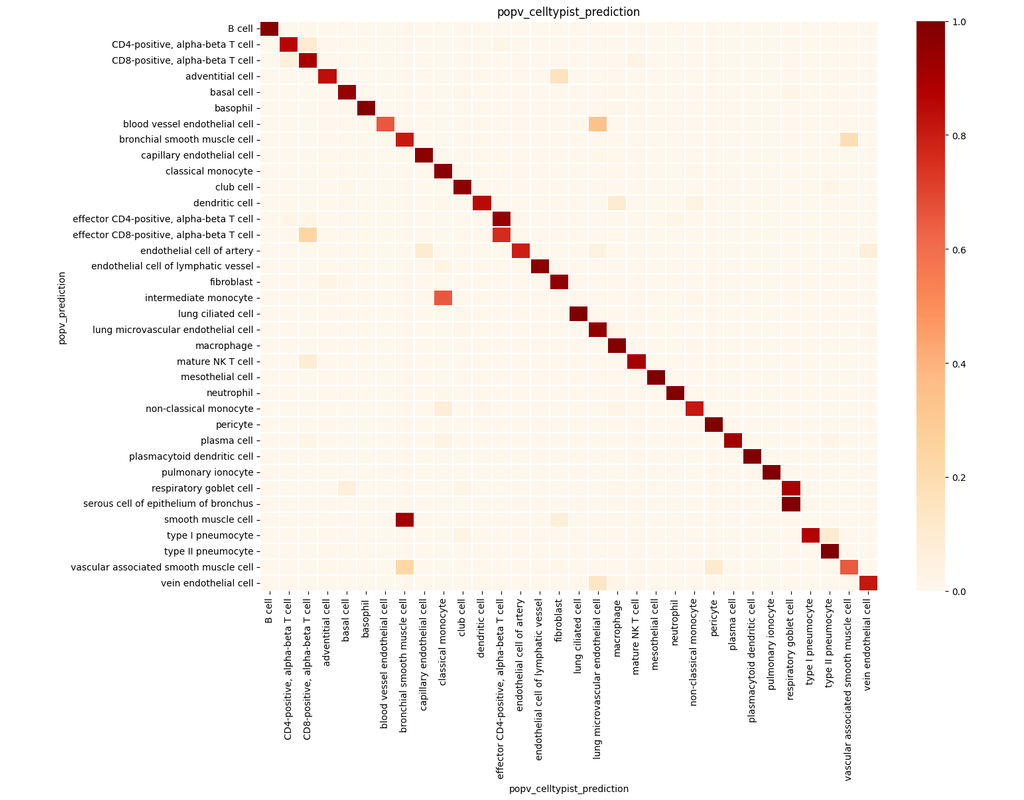
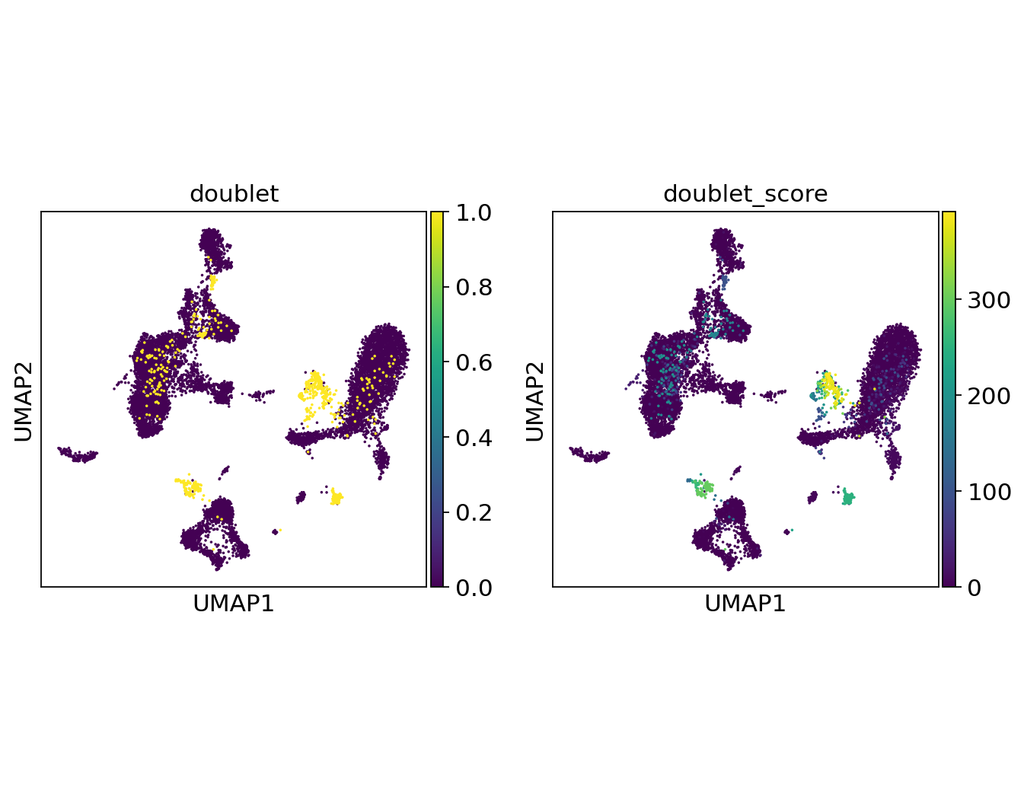
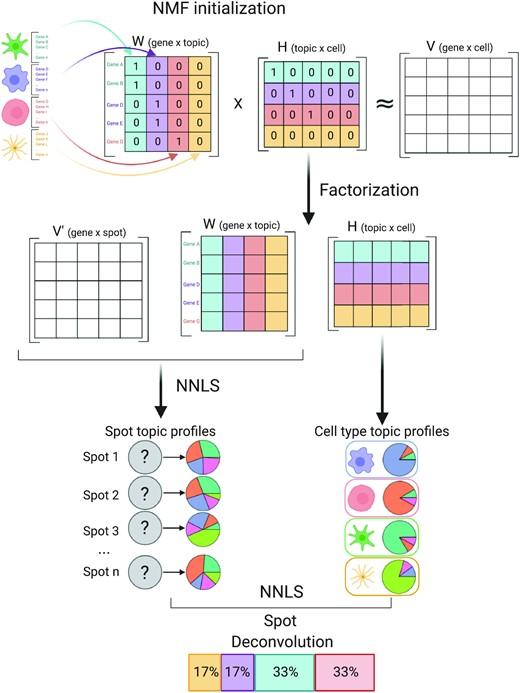
Spatially resolved gene expression profiles are key to understand tissue organization and function. However, spatial transcriptomics (ST) profiling techniques lack single-cell resolution and require a combination with single-cell RNA sequencing (scRN(More)