Notebooks
Premium
Trends
BioTuring
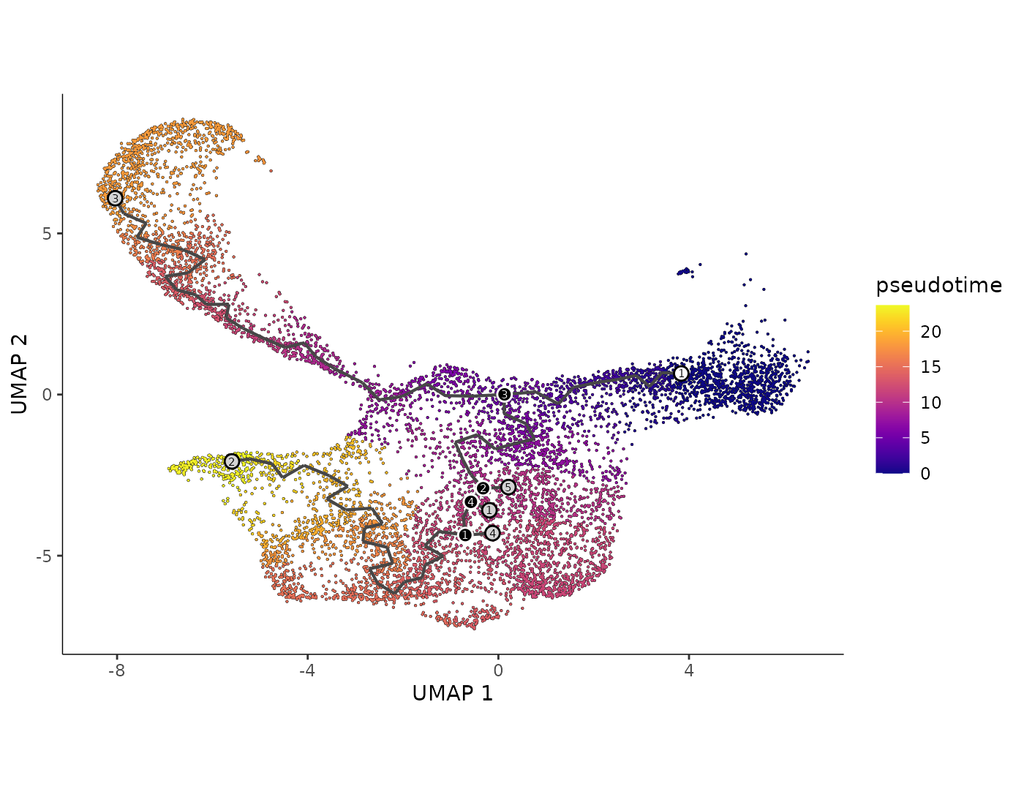
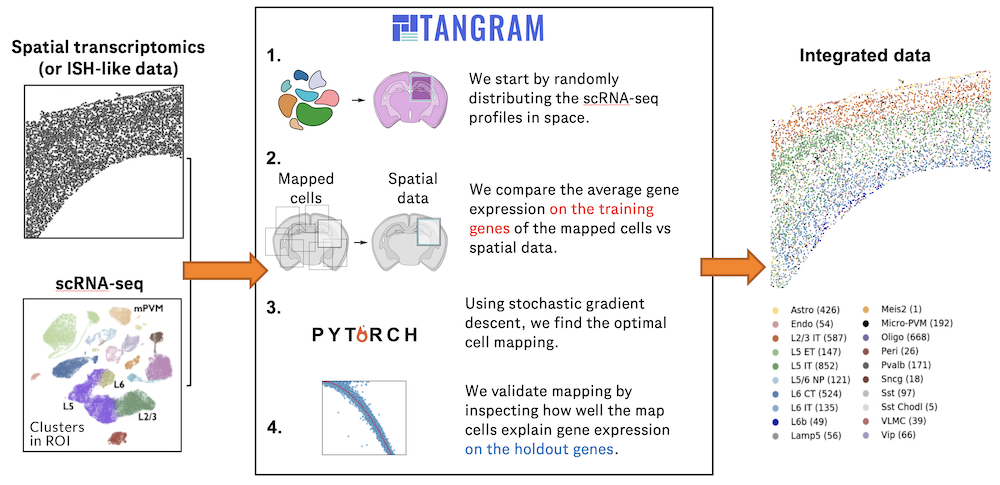
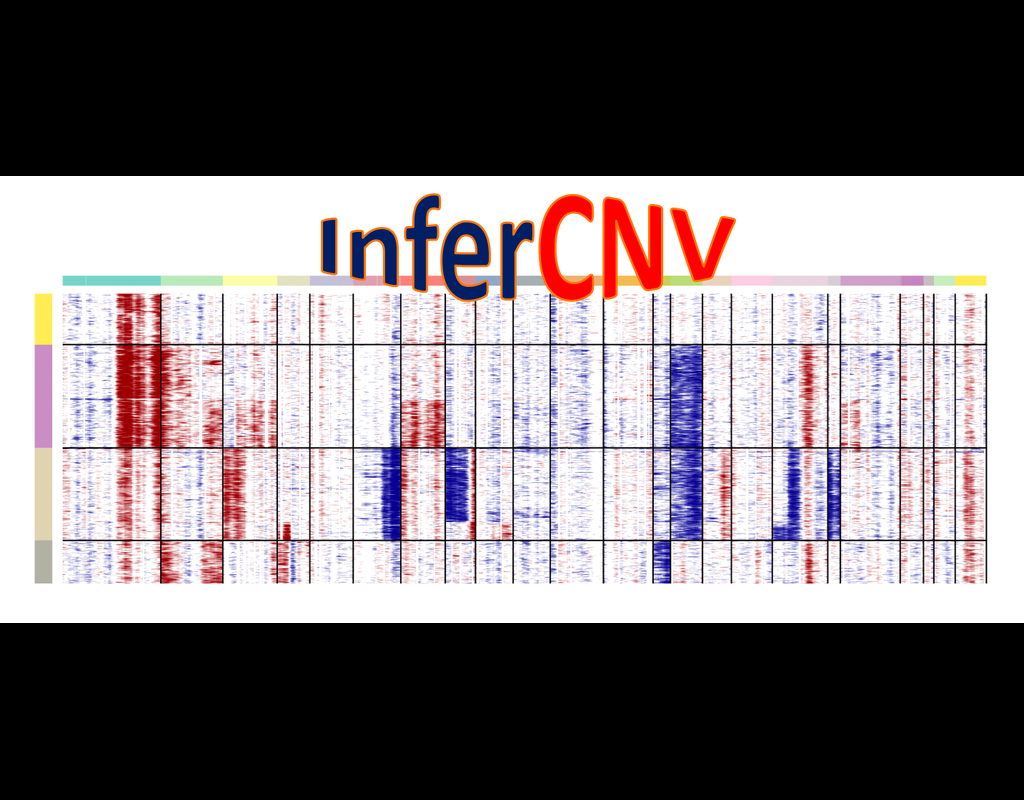
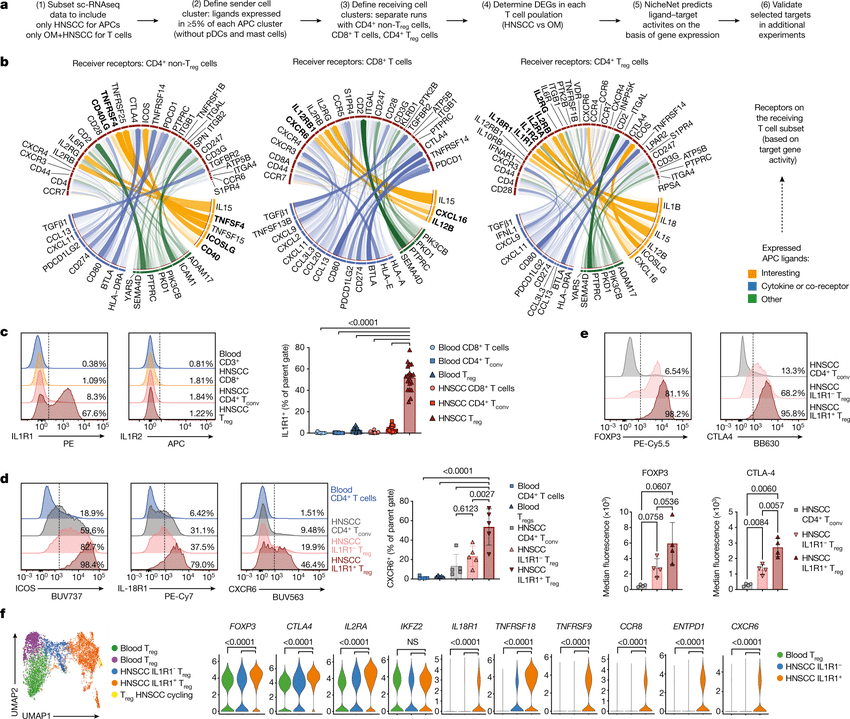
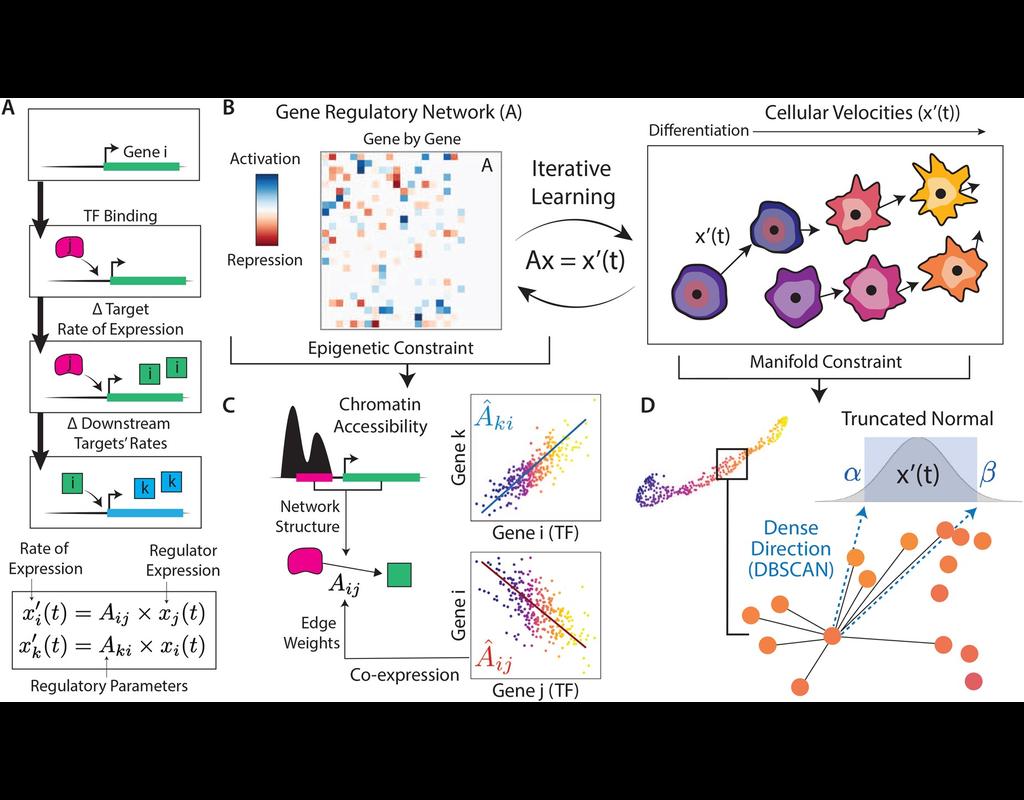
In the realm of transcriptional dynamics, understanding the intricate interplay of regulatory proteins is crucial for deciphering processes ranging from normal development to disease progression. However, traditional RNA velocity methods often overlo(More)