Notebooks
Premium
Trends
BioTuring
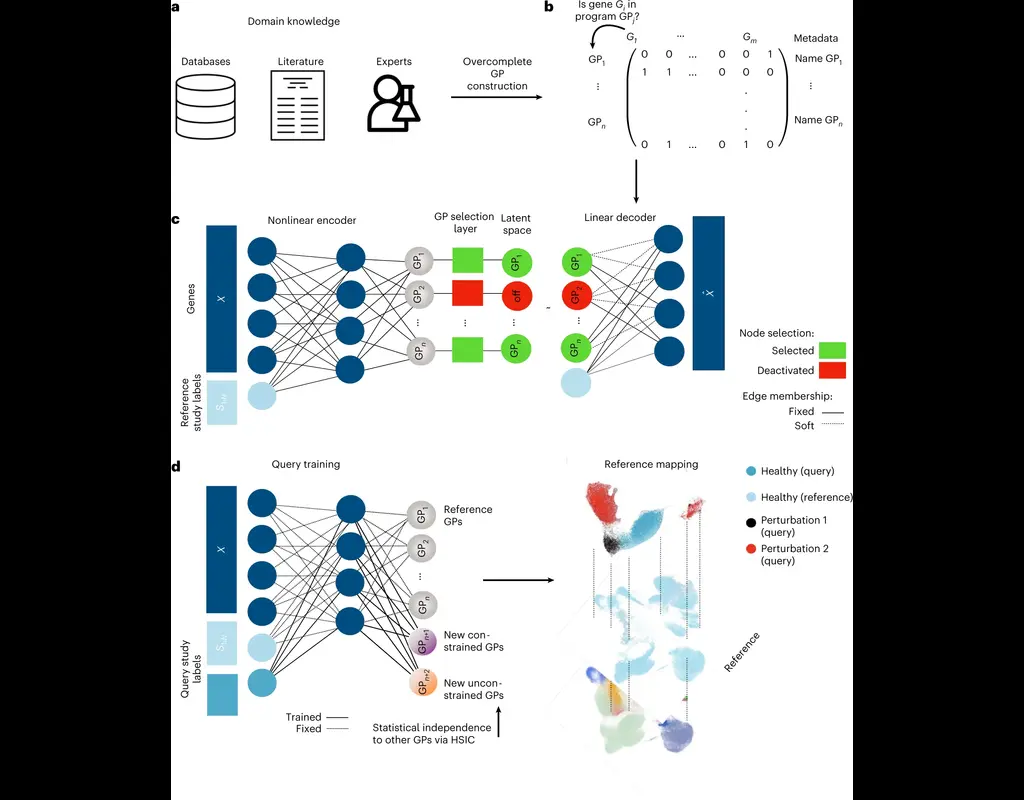
The development of large-scale single-cell atlases has allowed describing cell states in a more detailed manner. Meanwhile, current deep leanring methods enable rapid analysis of newly generated query datasets by mapping them into reference atlases. (More)