Notebooks
Premium
Trends
BioTuring
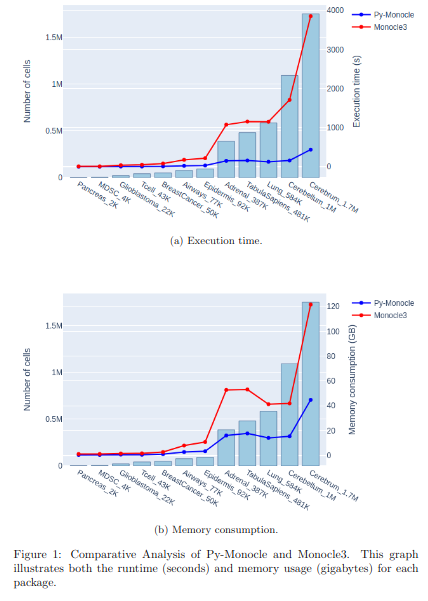
BioTuring Py-Monocle is a package tailored for computing pseudotime on large single-cell datasets. Implemented in Python and drawing inspiration from the Monocle3 package in R, our approach optimizes select steps for enhanced performance efficiency. (More)