Notebooks
Premium
Trends
BioTuring
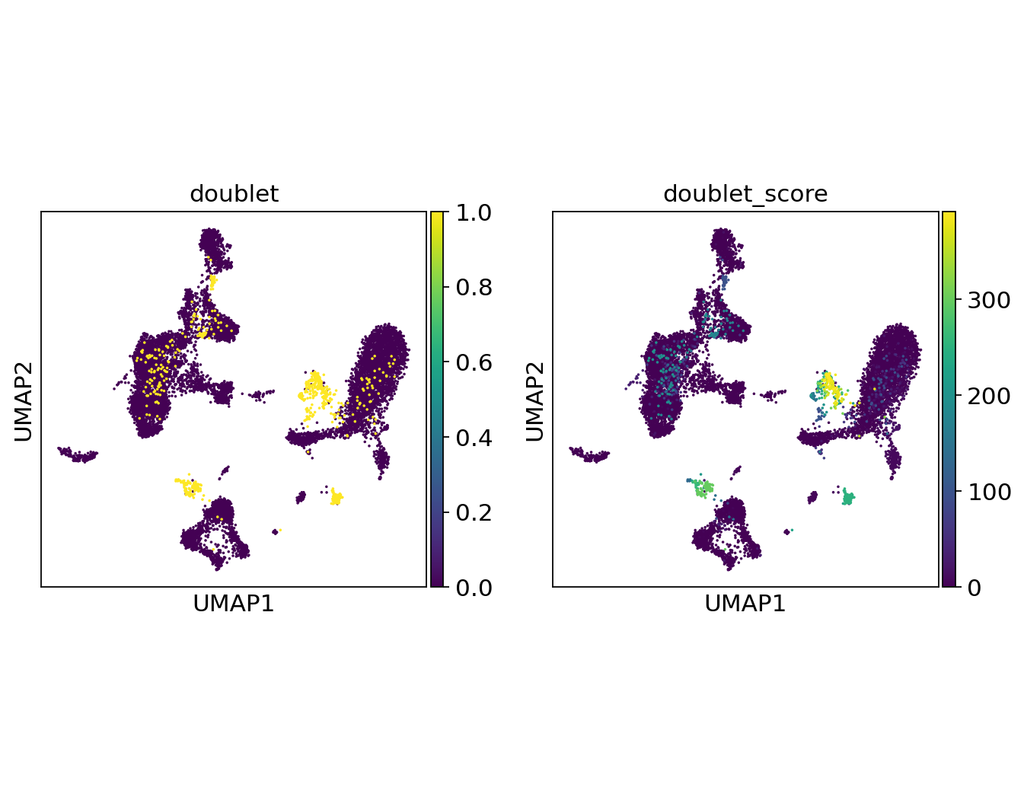
Doublets are a characteristic error source in droplet-based single-cell sequencing data where two cells are encapsulated in the same oil emulsion and are tagged with the same cell barcode. Across type doublets manifest as fictitious phenotypes that c(More)