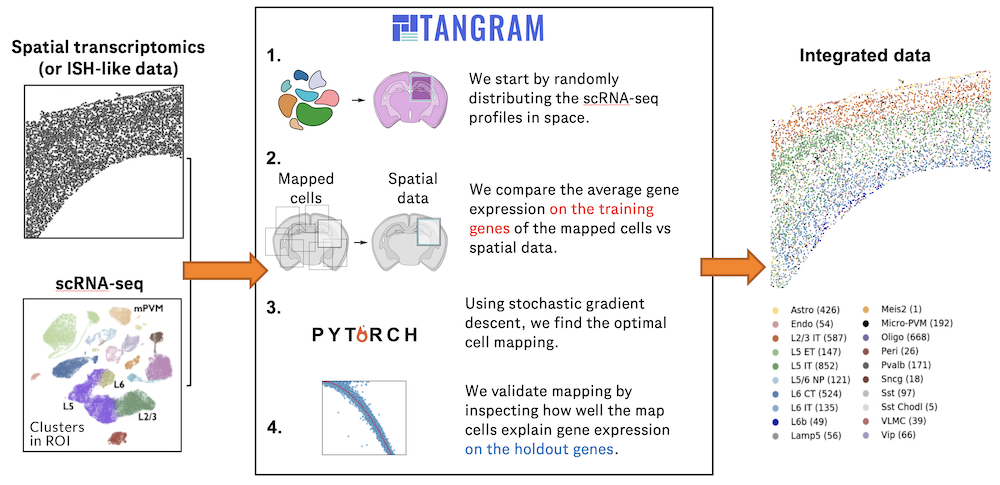
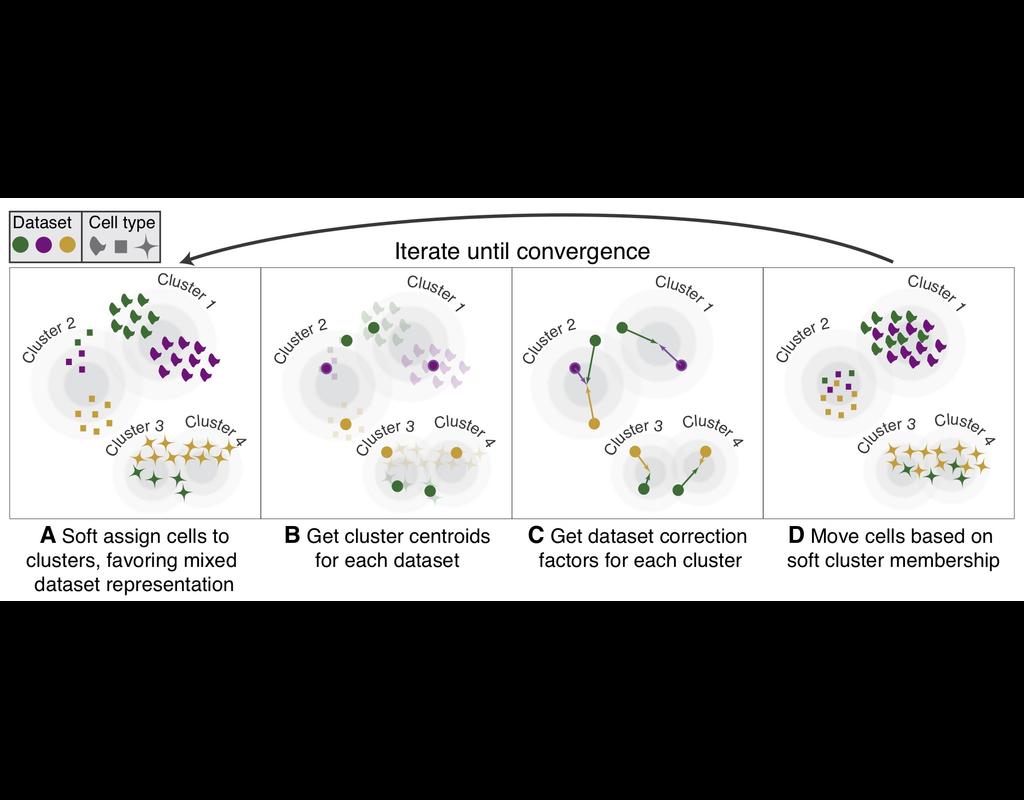
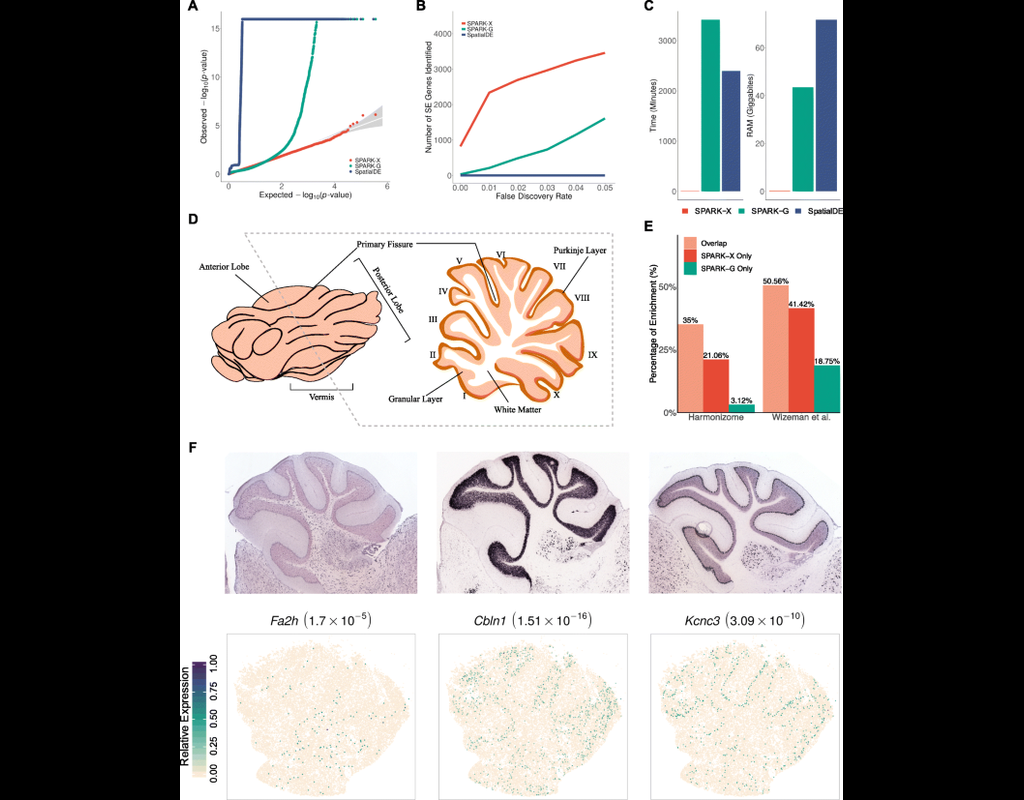
Notebooks
Premium
Trends
BioTuring
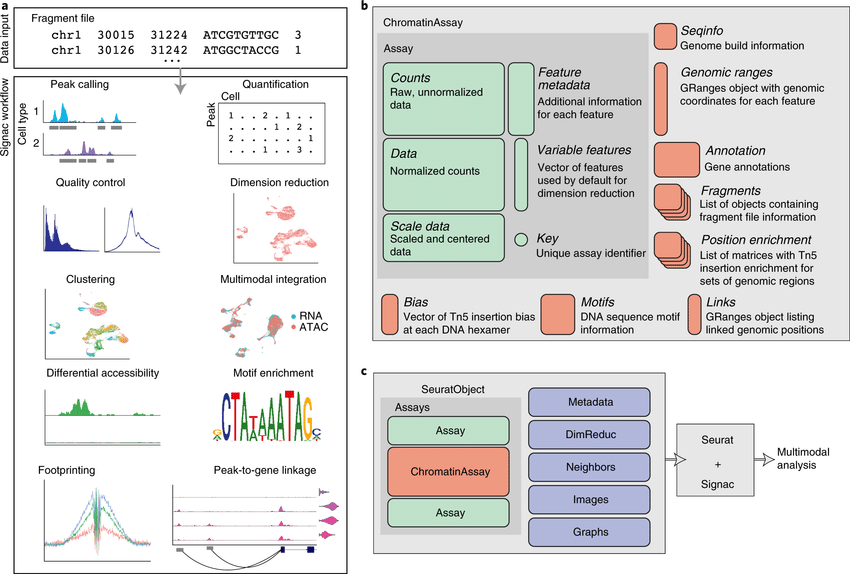
The recent development of experimental methods for measuring chromatin state at single-cell resolution has created a need for computational tools capable of analyzing these datasets. Here we developed Signac, a framework for the analysis of single-ce(More)