Notebooks
Premium
Trends
BioTuring
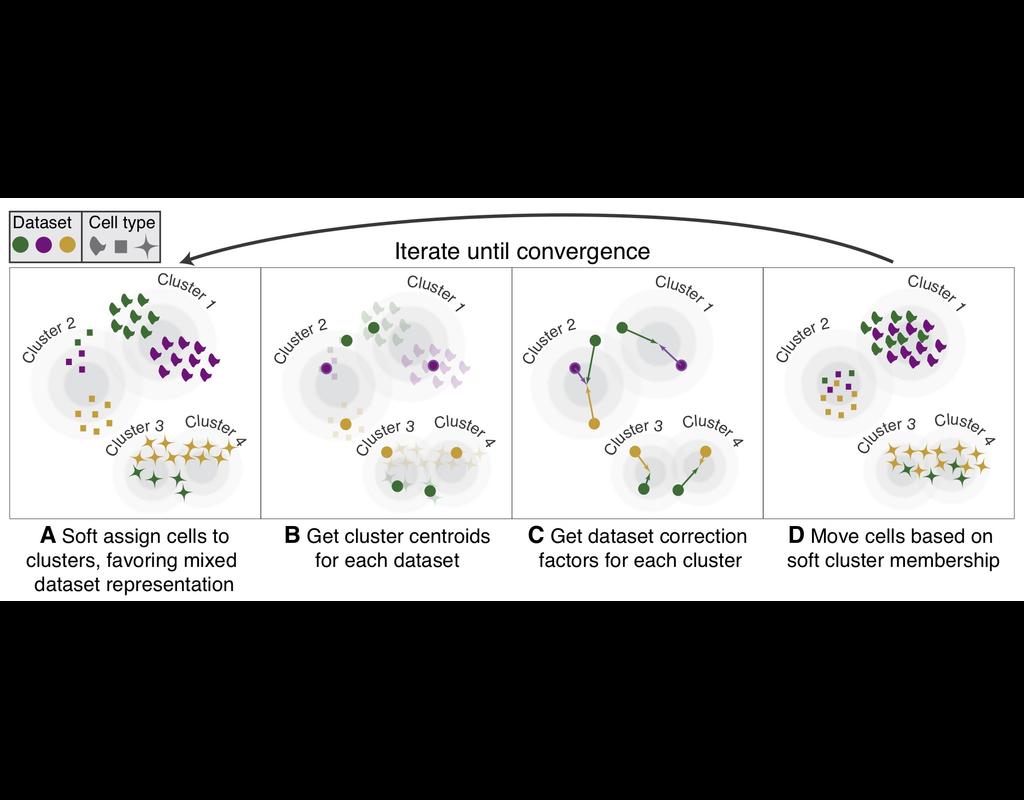
Single-cell RNA-seq datasets in diverse biological and clinical conditions provide great opportunities for the full transcriptional characterization of cell types.
However, the integration of these datasets is challeging as they remain biological(More)