Notebooks
Premium
Trends
BioTuring
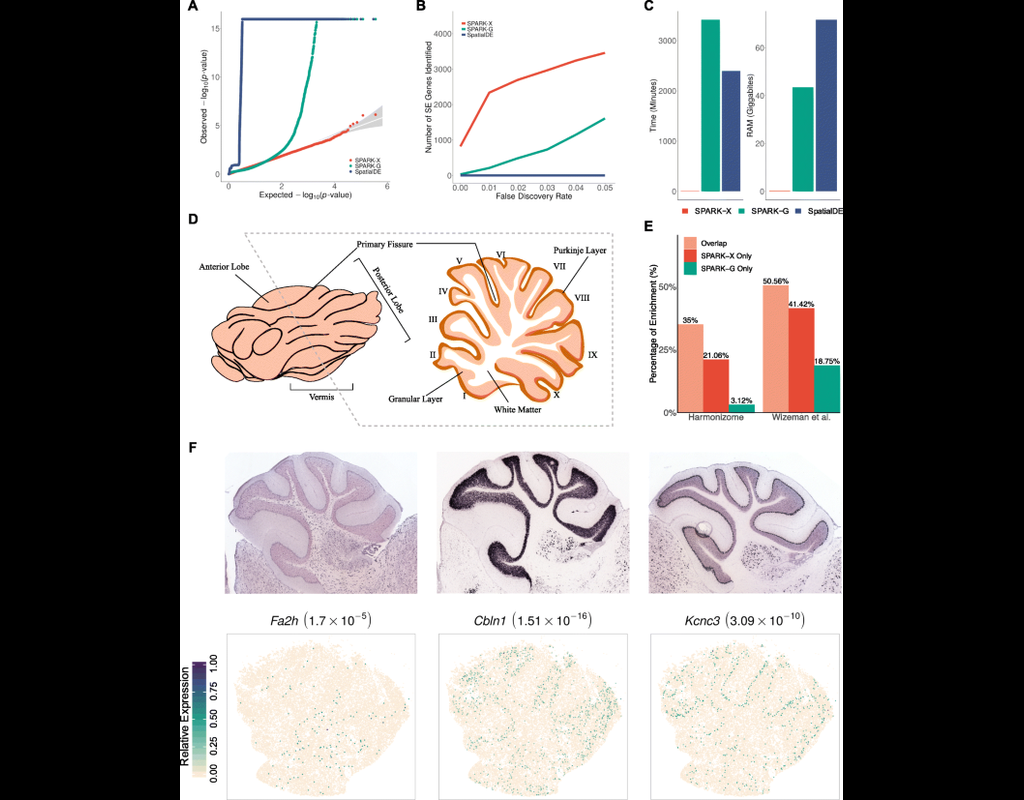
Spatial transcriptomic studies are becoming increasingly common and large, posing important statistical and computational challenges for many analytic tasks. Here, we present SPARK-X, a non-parametric method for rapid and effective detection of spati(More)