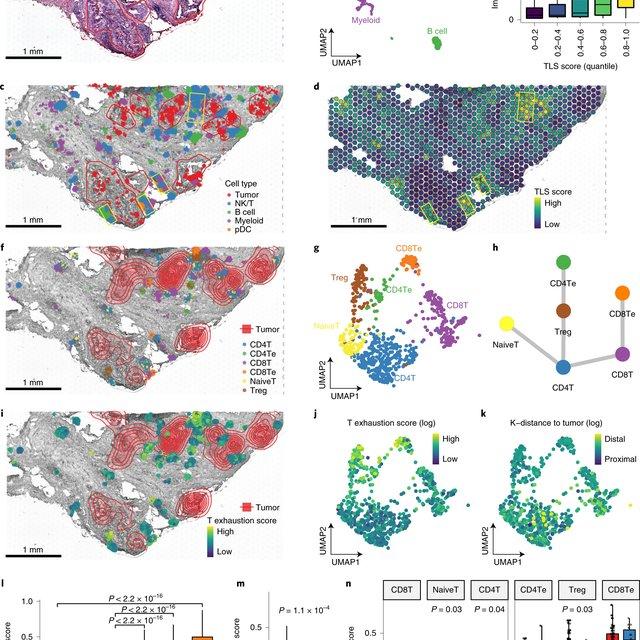
Notebooks
Premium
Trends
BioTuring
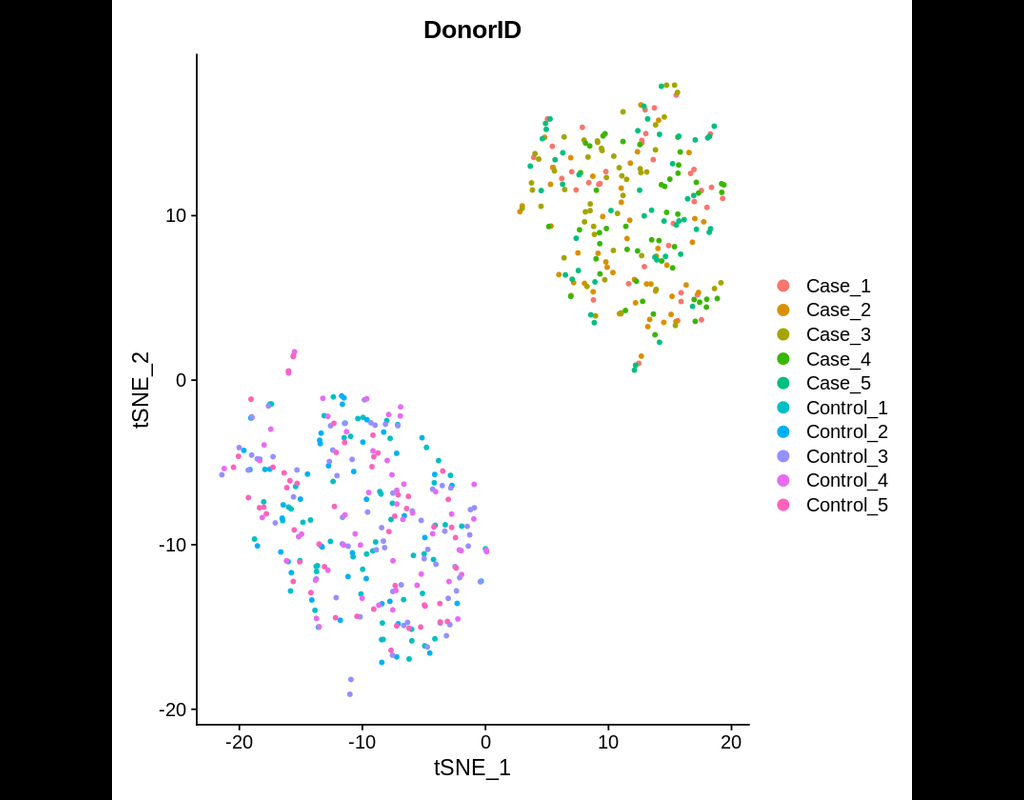
Power analyses are considered important factors in designing high-quality experiments. However, such analyses remain a challenge in single-cell RNA-seq studies due to the presence of hierarchical structure within the data (Zimmerman et al., 2021). As(More)