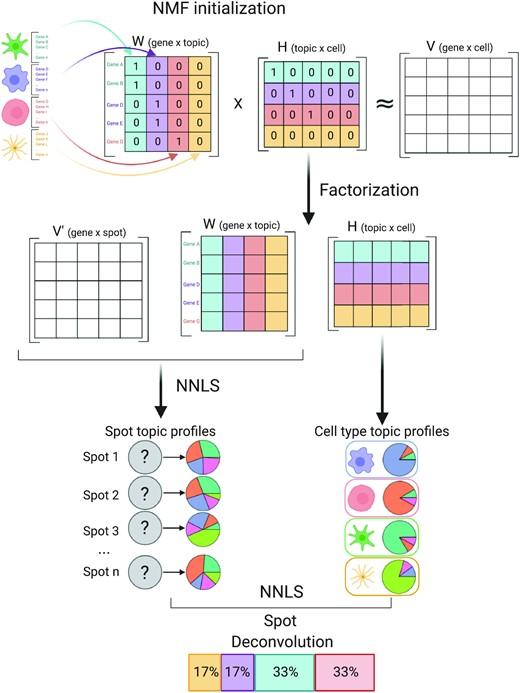
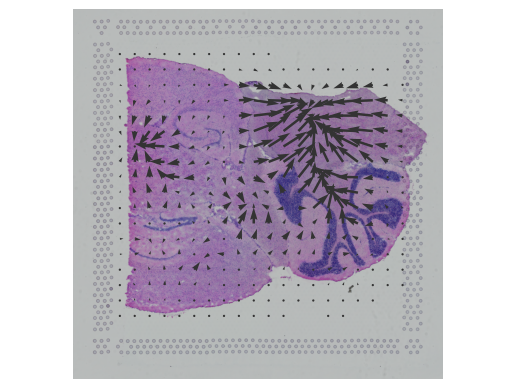
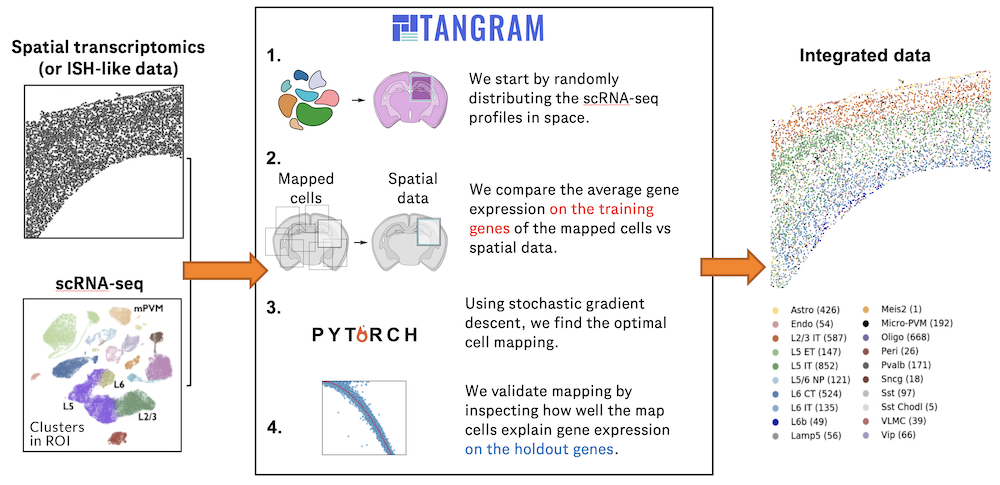
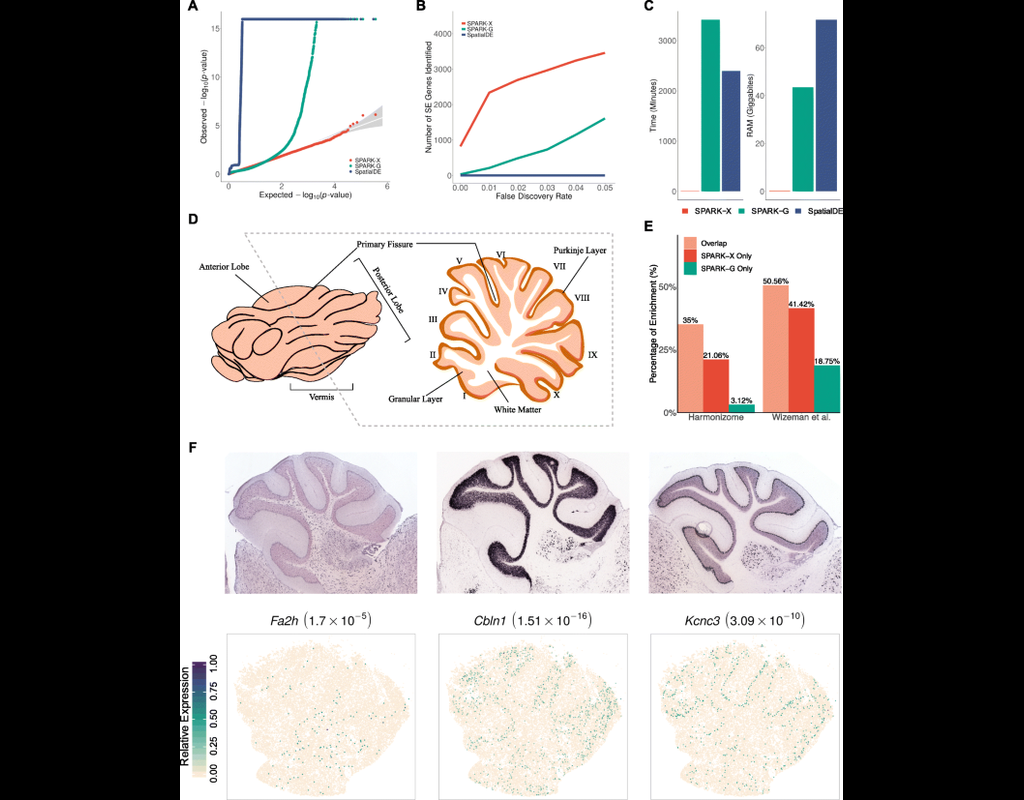
Notebooks
Premium
Trends
BioTuring
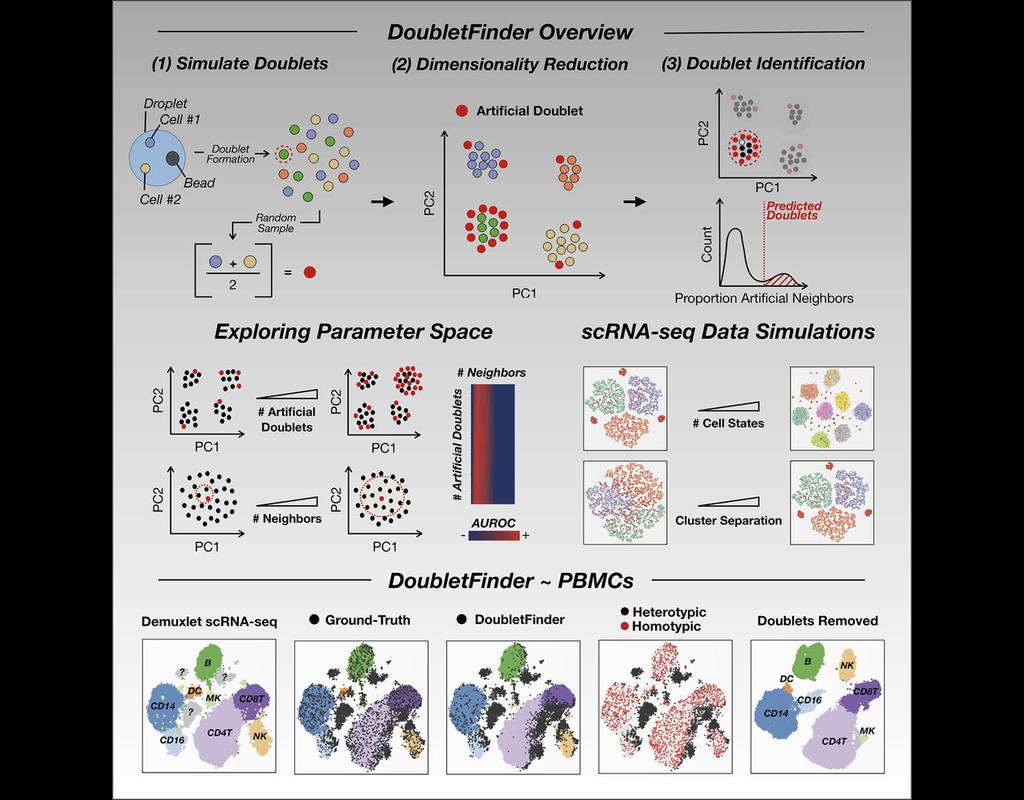
Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) data often encountered technical artifacts called "doublets" which are two cells that are sequenced under the same cellular barcode.
Doublets formed from different cell types or states are called heterotypic(More)