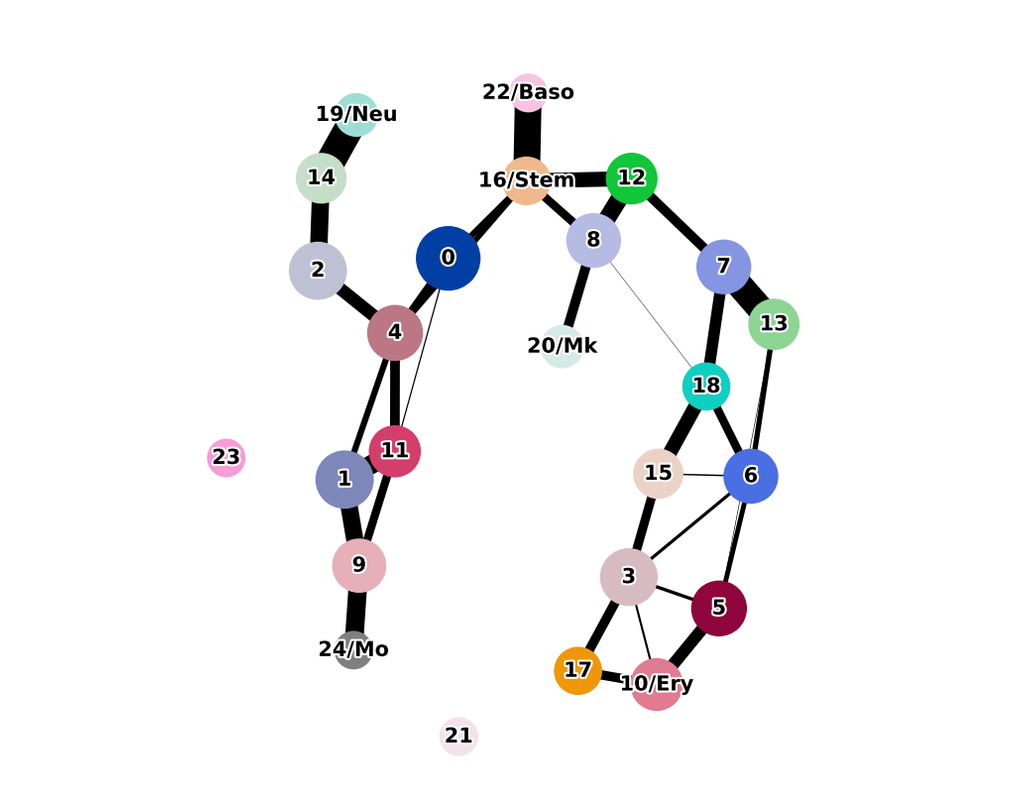
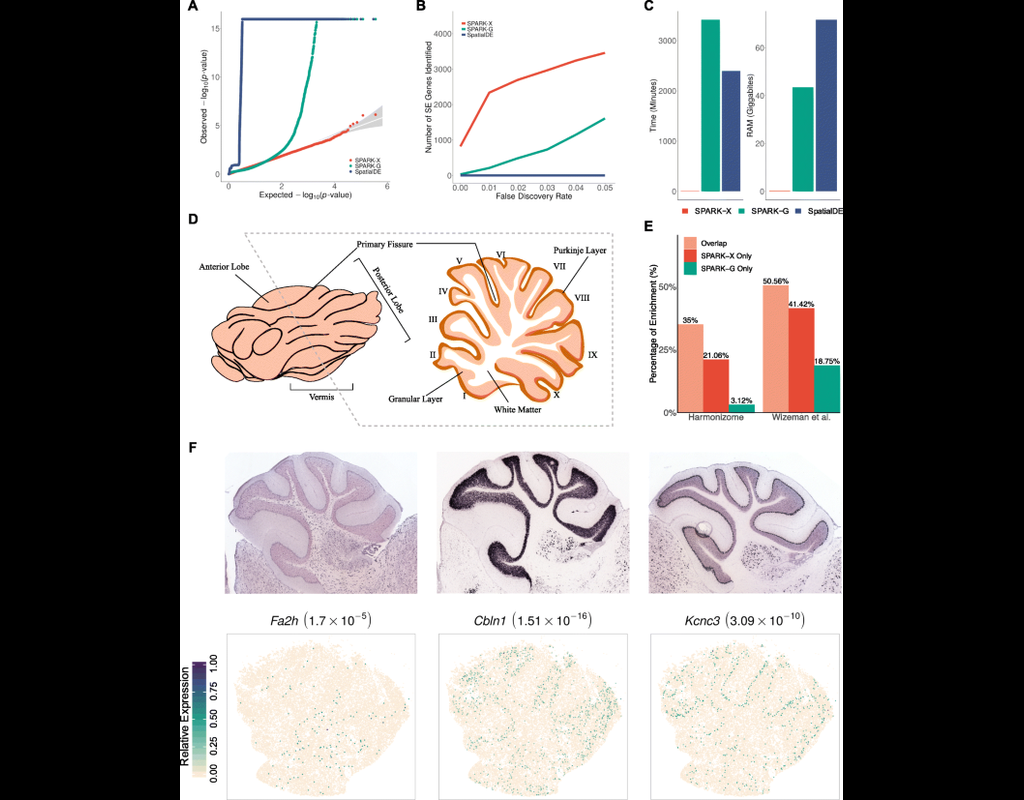
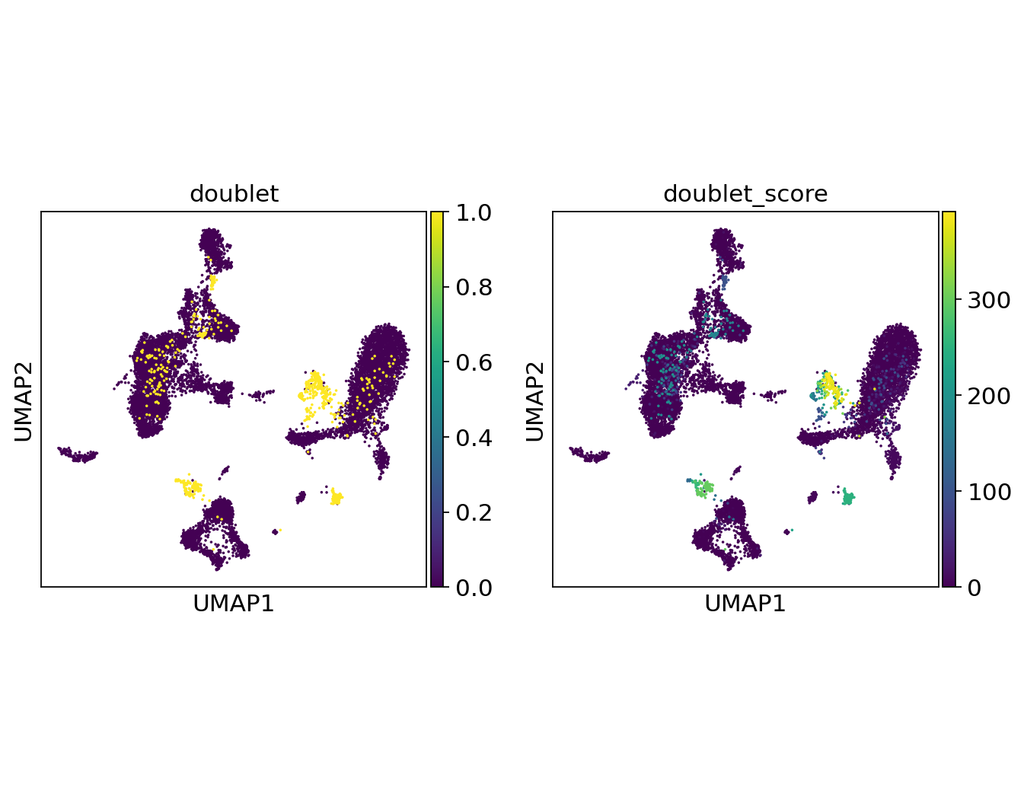
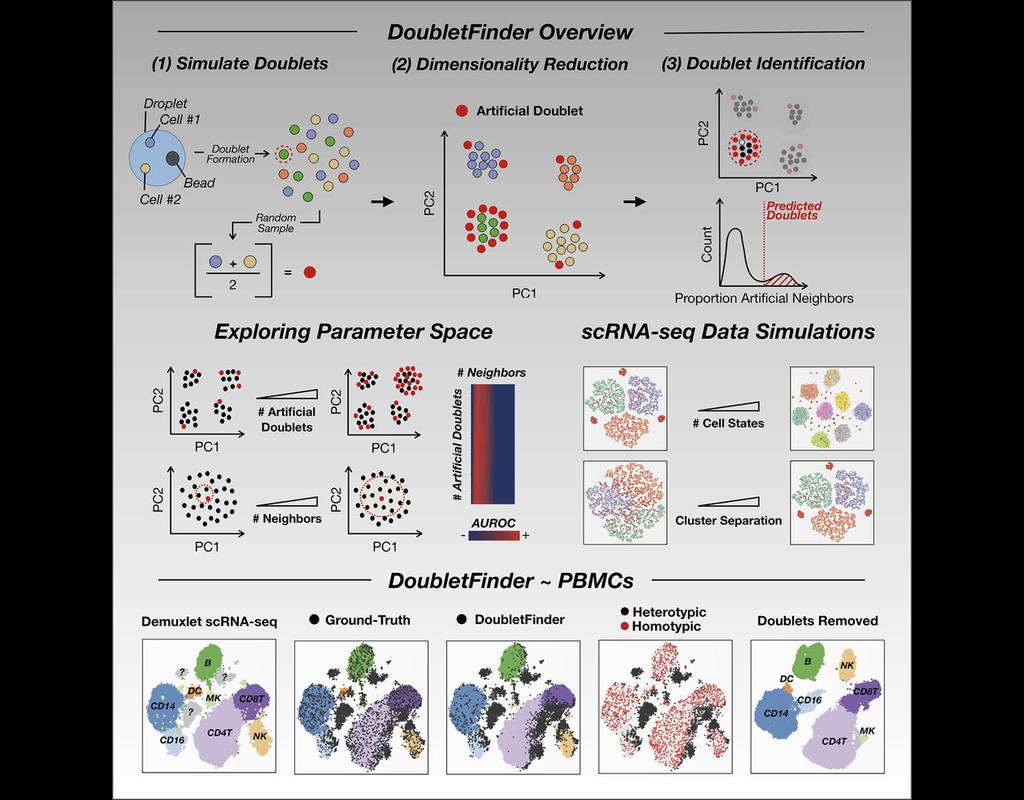
Notebooks
Premium
Trends
BioTuring
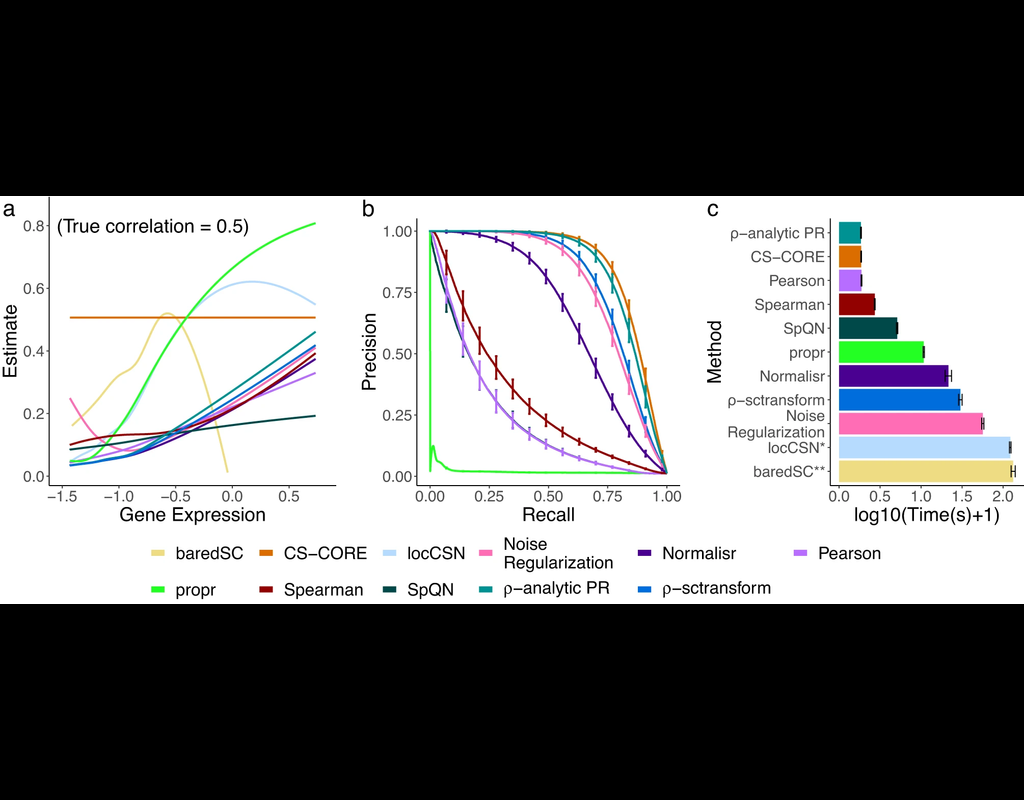
The recent development of single-cell RNA-sequencing (scRNA-seq) technology has enabled us to infer cell-type-specific co-expression networks, enhancing our understanding of cell-type-specific biological functions. However, existing methods proposed (More)