Notebooks
Premium
Trends
BioTuring
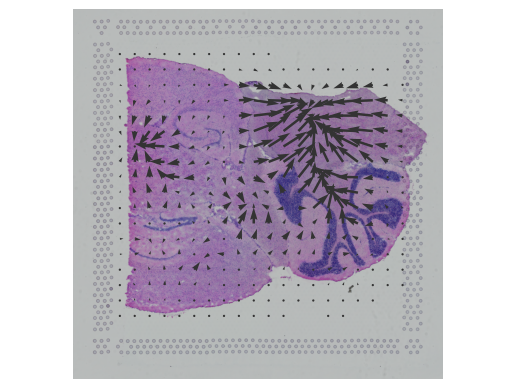
In this notebook, we present COMMOT (COMMunication analysis by Optimal Transport) to infer cell-cell communication (CCC) in spatial transcriptomic, a package that infers CCC by simultaneously considering numerous ligand–receptor pairs for either sp(More)